Technological solutions to reduce sediment in the Hornitos power plant intake

What we are looking for?
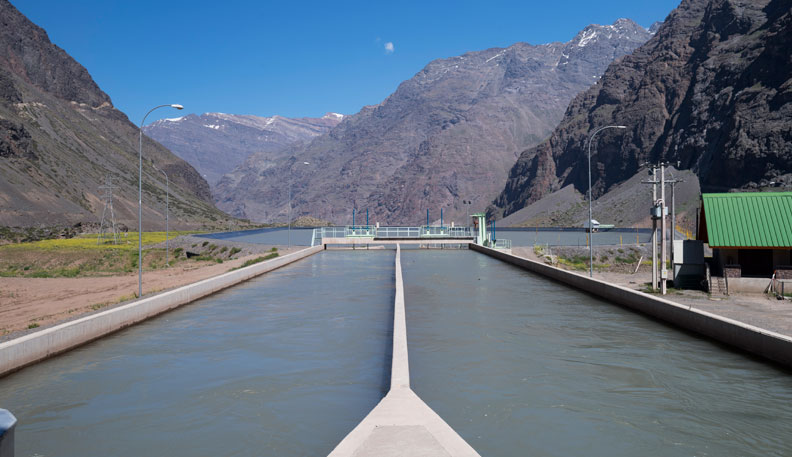
At the Colbún Aconcagua hydroelectric power plant complex, they face the constant challenge of sediment carried by the Aconcagua River. This issue becomes critical during droughts, when sediment levels increase.
The main impact of this sediment is that it causes erosion and wear on turbine components, reducing their efficiency and requiring frequent maintenance and repairs, especially for the impeller.
The company is looking for a technological solution to reduce fine sediment upstream of the first power plant (Hornitos), specifically in the area after the water intake. The solution should remove a large portion of the sediment from the water and discharge it back into the river (in-line), considering the existing environmental permits.

How will we evaluate your solution?
The key performance indicator (KPI) they aim to impact is the reduction of dissolved solids in the water by at least 30% after the water intake. The flow rate reaching the intake is approximately 8 m³/s, with a variable sediment concentration between 500 mg/L and 50.000 mg/L.
The location where the sediments should be removed is about 10-15 meters from the Aconcagua River, where the extracted sediments must be discharged.
This impact will lead to a decrease in runner wear and reduce the need for maintenance, repairs, and component replacement for the hydroelectric turbine.